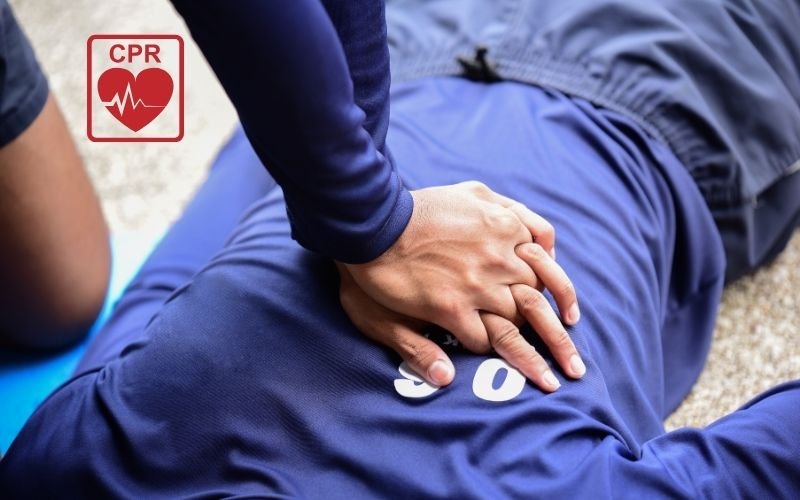
Each second counts when the heartbeat of a person stops. In a short period of time, brain damage may happen without oxygen abundant blood. CPR, or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, has proven its efficiency in the above cases and can be used to maintain a drain of blood till medical assistance is availed.
CPR is not only a first aid technique. Learning this is a life-saving skill that anyone can acquire to fight back. Being aware of the CPR procedure can be the difference between life and death, particularly in an instance of cardiac arrest or instantaneous collapse triggered by a heart attack. Here in this article, a top cardiology specialist in Delhi explains the CPR process & steps:
When CPR is Needed?
CPR is performed when a person:
- Has no pulse or heartbeat
- Is not breathing or is gasping irregularly
- Becomes unresponsive after collapse
Cardiac arrest can happen after drowning, severe injury, electrocution or certain medical conditions. In these moments, starting CPR quickly increases the chances of survival
The CPR Process: Basic Principles
The CPR process follows a clear sequence. International guidelines recommend the CAB order C for compressions, A for airway and B for breathing
Before starting always check the scene for safety and call emergency services. If possible have someone bring an automated external defibrillator (AED) as it can help restart the heart
CPR Steps for Adults
1. Check Responsiveness and Breathing
Gently tap the person’s shoulder and shout to see if they respond. Look for normal breathing. If they are unresponsive and not breathing normally, act immediately
2. Call for Help
Dial emergency services or instruct someone nearby to do so. Mention the situation clearly so that paramedics arrive prepared. Go to the best heart hospital in Delhi asap.
3. Start Chest Compressions
Place the heel of one hand in the center of the chest. Place your other hand on top and interlock fingers. Keep arms straight and shoulders above your hands. Press down hard and fast about 2 inches deep at 100–120 compressions per minute. Let the chest rise fully between presses
4. Open the Airway
Tilt the head back slightly and lift the chin. This helps air pass into the lungs
5. Give Rescue Breaths
Pinch the nose shut, seal your mouth over theirs, and blow in for about one second. Watch for the chest to rise. Give two breaths after every 30 compressions
Continue the cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until help arrives or the person starts breathing
Hands-Only CPR
If you are untrained or uncomfortable giving rescue breaths you can perform hands-only CPR. Push hard and fast in the center of the chest without stopping for breaths. This method is still highly effective in the first few minutes after collapse
CPR for Children and Infants
While the basic approach is similar, there are important differences for younger patients:
- Use one hand for chest compressions on children, and two fingers for infants
- Compressions should be about 1.5 inches deep for infants and 2 inches for children
- Give gentler rescue breaths
Knowing these adjustments ensures CPR is safe and effective for all ages
Common Mistakes to Avoid in cases of heart attack
Even with good intentions CPR can be less effective if done incorrectly. Avoid these mistakes:
- Not pressing deep enough
- Pausing compressions too long
- Forgetting to call for help before starting
- Leaning on the chest without letting it fully rise
Training with a certified heart specialist can help build the right technique and confidence
CPR is a skill that turns ordinary people into life-savers. It keeps oxygen flowing, buys critical time and gives patients a chance to survive until hospital care is available
For anyone in Delhi, Primus Hospitals offers advanced emergency and cardiac care. As a trusted Cardiology hospital in Delhi it combines expert doctors, modern technology and rapid response teams to handle heart emergencies with precision. Whether it’s CPR for heart attack cases or advanced cardiac treatment the hospital’s focus remains on saving lives
Learning CPR is not just a medical skill it’s an act of responsibility. In the right moment your quick action can mean someone’s tomorrow