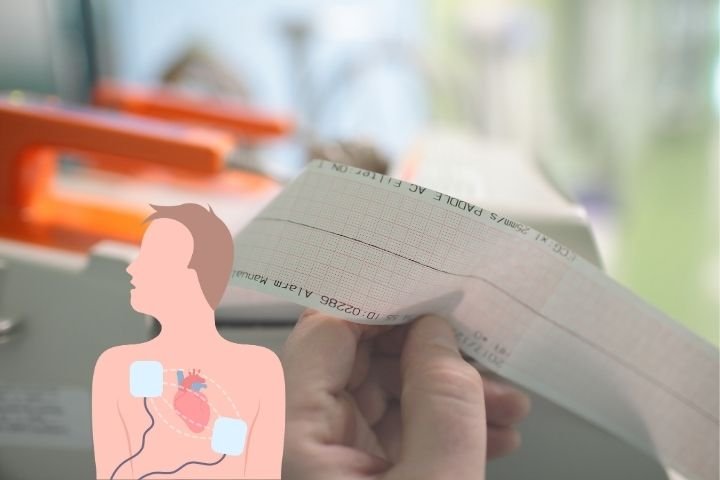
Blunt chest pain often scares people. Many feel confused when they hear terms like defibrillation or cardioversion. These words sound heavy, and the idea of an electric shock feels scary too. But both methods save lives, and both help the heart return to a safer rhythm. When patients sit with me, they often ask the same thing in a soft voice, “Doctor, what is cardioversion? And how is it different from defibrillation?”
So, this long guide breaks things down. We will explain the difference between cardioversion vs defibrillation, how each works, and when doctors use them. We will try to make everything clear. The idea is to help you understand the process before you visit a heart specialist in Delhi or any cardiology hospital in Delhi.
Why the Heart Loses Rhythm?
The heart moves blood with a steady beat. When the beat turns fast or irregular, the body feels weak. Some people feel dizzy; others feel a sudden drop in energy. You may hear conditions like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or flutter. These issues disturb the heart’s signals. When this happens doctors restore rhythm with cardioversion or defibrillation
Both use electric current. But the timing, force, and purpose are very different.
What Is Cardioversion?
Cardioversion resets the heart’s rhythm using a controlled shock. The shock is low-power and timed. Doctors match it with the heart’s electrical cycle. This timing helps avoid further rhythm issues
When Do Doctors Use Cardioversion?
Cardioversion works best for rhythm issues that start in the upper chambers. These include:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- Supraventricular tachycardia
The goal is to bring the rhythm back to normal without strong force.
Types of Cardioversion
Doctors choose from two forms:
- Electrical cardioversion
A short burst of energy resets the rhythm. The patient sleeps under light anesthesia. - Synchronized cardioversion
This shock matches the R-wave of the ECG. It keeps the beat steady during correction.
Both methods work well in expert hands. Many patients in Delhi recover within hours.
What Is Defibrillation?
Defibrillation looks similar from outside, but the action inside the heart is very different.
Defibrillation uses a stronger electric shock. It is not timed. Doctors use it only in life-threatening cases. When the heart quivers or stops pumping blood well, defibrillation steps in fast.
When Do Doctors Use Defibrillation?
This method treats dangerous rhythm issues. These include:
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
- Sudden cardiac arrest
In these cases, the heart loses control and shakes without moving blood. A strong shock stops this chaos.
Cardioversion vs Defibrillation: The Core Difference
Let me explain this part as I often explain it to patients in Delhi. The heart moves with an electrical cycle. Cardioversion respects this cycle. Defibrillation interrupts it. That’s the main difference.
Key Differences at a Glance
- Timing: Cardioversion is timed. Defibrillation is not.
- Urgency: Cardioversion treats stable patients. Defibrillation treats emergencies.
- Shock level: Cardioversion uses low energy. Defibrillation uses high energy.
- Purpose: Cardioversion adjusts. Defibrillation resets.
How Heart specialists Decide?
Doctors study the ECG. They check the pulse, symptoms, history, and medication use. One wrong step can harm the heart. So the choice depends on the exact rhythm and the patient’s stability.
Why Delhi Patients Often Confuse Both
Delhi residents often visit clinics with fear in their eyes. Families hear “shock treatment” and imagine the worst. The city has many advanced heart hospitals in Delhi, but the terms still confuse people.
The confusion grows because both methods use pads and electric current. But the goals differ. Cardioversion is safe for planned use. Defibrillation is only for emergencies, often without delay.
Preparation Before Cardioversion
Cardioversion often takes place in a controlled room. Doctors guide the patient with calm steps. Some key steps include:
- Checking blood tests
- Reviewing medication history
- Performing imaging if needed
- Giving light anesthesia for comfort
Patients usually return home the same day.
Safety Measures During Defibrillation.
Defibrillation follows strict rules because every second matters. When someone collapses the team checks:
- Consciousness
- Breathing
- Pulse
- ECG rhythm
- Oxygen level
The shock is delivered fast and there is no waiting time. It saves the heart before damage grows
Cardioversion Surgery Is Rarely Required
People ask about cardioversion surgery or defibrillation surgery. The truth is that both techniques are not traditional surgeries. They use devices and controlled electric currents. No incisions, no stitches, and no long recoveries.
Still, severe heart rhythm issues may later require procedures like ablation or device implants.
Choosing the Right Hospital in Delhi
A patient should choose a center with advanced monitoring, skilled emergency teams, and experienced cardiologists. Facilities matter during rhythm correction.
Many people look for the:
- best heart hospital in Delhi
- top cardiology hospital in Delhi
- trusted heart specialist in Delhi
The right doctor ensures safety before, during, and after the shock procedure.
Both cardioversion and defibrillation save lives, but they work in very different ways. One resets a rhythm gently. The other stops dangerous chaos in the heart. If you face rhythm issues always follow a specialist’s advice
Primus Hospitals known for its skilled cardiac teams and modern systems, offers advanced care for rhythm disorders. Our experts guide patients through diagnosis, treatment and long-term support with strong clinical experience. The right care at the right time keeps the heart safe, steady, and strong
FAQs
It resets an abnormal rhythm using a timed electric shock. The shock is mild and controlled.
Doctors use anesthesia, so most patients do not feel the shock. Some feel mild soreness later.
Cardioversion uses low energy and works on stable patients. Defibrillation uses high energy and treats emergencies
They correct rhythm. But long-term care may still be needed. Some patients need medicine or ablation later.
Yes. Many cardiology hospitals use global-standard equipment and trained specialists.