Mechanical ventilation is a vital therapeutic practice in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patient treatment. This device maintains proper oxygenation and carbon dioxide clearance through breathing support or replaces of spontaneous breathing. This article written under the guidance of a critical care specialist in Delhi explains ICU, ventilation types and ventilator modes for optimal treatment.
Types of Ventilation or Ventilator in ICU
In the ICU, mechanical ventilation can be broadly categorized into two types: invasive and non-invasive.
Invasive Ventilation
Invasive ventilation involves the insertion of an endotracheal tube (ETT) into the patient’s airway. This method is typically used when patients cannot maintain adequate gas exchange on their own.
Key Features:
- Airway Access: Direct access via ETT
- Indications: Severe respiratory failure, inability to protect the airway
- Advantages: Precise control over ventilation parameters
- Disadvantages: Risk of infection, airway injury
Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
Ventilatory support delivered through non-invasive settings does not require intubation because patients use interfaces like masks.
Key Features:
- Airway Access: External interfaces (e.g., masks)
- Indications: Mild to moderate respiratory distress, COPD exacerbations
- Advantages: Reduced risk of infection, patient comfort
- Disadvantages: Potential for air leaks, less control over ventilation
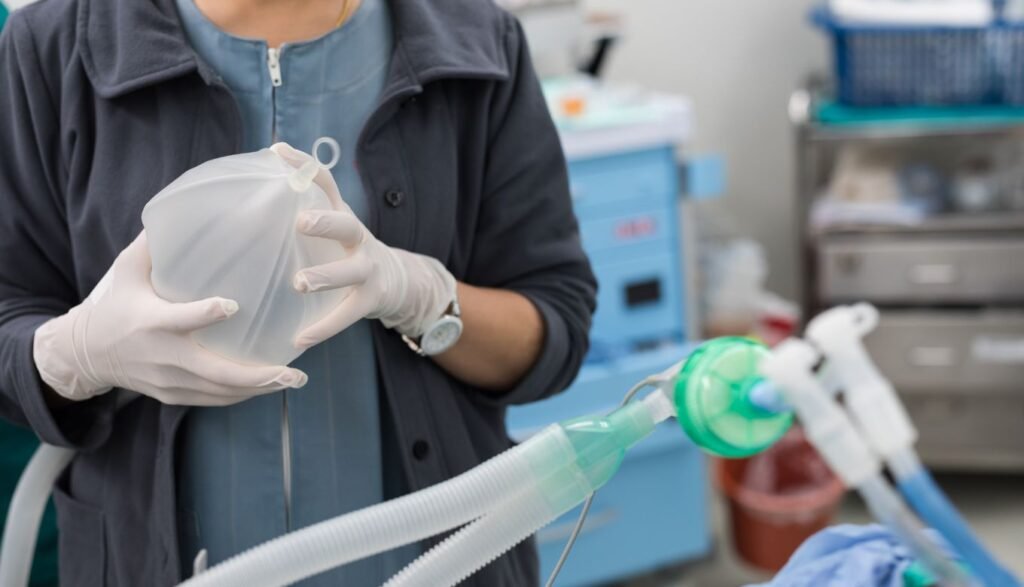

Modes of Ventilation in ICU
A ventilator assists patient breathing through various ventilation modes. Each patient receives tailored ventilation settings because of the individualized mode selection.
Volume-Controlled Ventilation (VCV)
In VCV, the ventilator delivers a preset tidal volume with each breath, regardless of the pressure required.
Key Features:
- Control Variable: Volume
- Indications: Patients requiring consistent tidal volumes
- Advantages: Ensures stable minute ventilation
- Disadvantages: Potential for high airway pressures
Pressure-Controlled Ventilation (PCV)
PCV delivers breaths at a preset pressure, with the volume varying based on lung compliance.
Key Features:
- Control Variable: Pressure
- Indications: Patients with poor lung compliance, such as ARDS
- Advantages: Limits peak airway pressures
- Disadvantages: Variable tidal volumes
Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV)
PSV functions as a spontaneous mode which supplies predetermined pressure support for all breaths triggered by the patient.
Key Features:
- Control Variable: Pressure
- Indications: Patients with adequate spontaneous breathing efforts
- Advantages: Enhances patient comfort, reduces work of breathing
- Disadvantages: Requires reliable patient effort
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
The mandatory breath sequence of SIMV functions in harmony and time with a patient’s breathing movements.
Key Features:
- Control Variable: Volume or Pressure
- Indications: Weaning patients from mechanical ventilation
- Advantages: Allows spontaneous breathing between mandatory breaths
- Disadvantages: Potential for increased work of breathing
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
CPAP provides a constant positive airway pressure throughout the respiratory cycle in spontaneously breathing patients.
Key Features:
- Control Variable: Pressure
- Indications: Obstructive sleep apnea, mild respiratory distress
- Advantages: Keeps airways open, improves oxygenation
- Disadvantages: Patient must breathe spontaneously
ICU Ventilator Modes Chart
The ICU ventilator chart explains all modes and their properties for patients based on needs
| Mode | Control Variable | Patient Effort | Key Indications |
| Volume-Controlled Ventilation (VCV) | Volume | Not required | Consistent tidal volume needed |
| Pressure-Controlled Ventilation (PCV) | Pressure | Not required | Poor lung compliance |
| Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) | Pressure | Required | Spontaneous breathing support |
| Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV) | Volume/Pressure | Required | Weaning from mechanical ventilation |
| Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) | Pressure | Required | Obstructive sleep apnea |
How Ventilation Modes Help Patients?
Selecting the appropriate ventilation mode is vital for patient recovery in the ICU.
Enhancing Oxygenation and Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation ensures adequate oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal, especially in patients with respiratory failure
Reducing Work of Breathing
Modes like PSV assist patients by decreasing the effort required to breathe, promoting comfort and reducing fatigue
Protecting Lung Function
PCV helps in limiting peak airway pressures, reducing the risk of ventilator-induced lung injury
Facilitating Weaning
SIMV allows patients to gradually resume spontaneous breathing, aiding in the transition off mechanical support
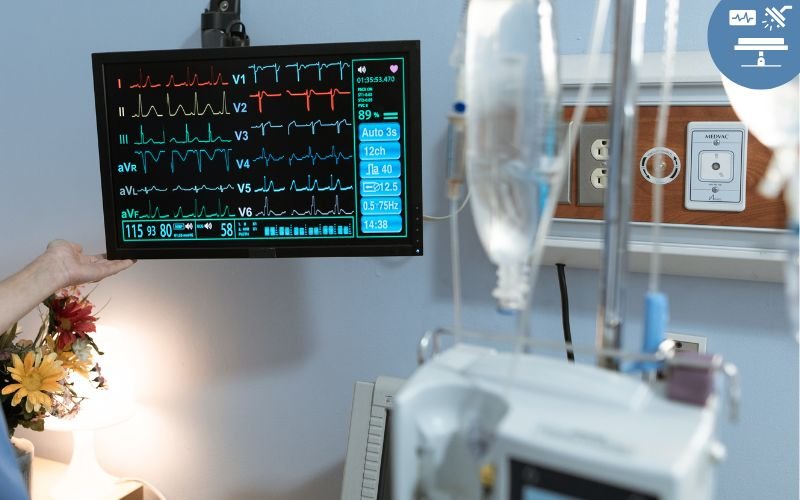
ICU Equipment and Monitoring
Effective mechanical ventilation relies on advanced ICU equipment and vigilant monitoring.
ICU Ventilator Bed in Delhi
The ventilator is a sophisticated machine that delivers breaths to patients based on the selected ventilation mode and patient needs. It regulates oxygen levels, pressure, and breathing rate to ensure optimal respiratory support.
ICU Monitor
An ICU monitor continuously tracks vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and blood pressure. This ensures immediate detection of any complications, allowing prompt medical intervention.
ICU Room Hospital Setup
An ICU room is equipped with advanced life-support systems, including ventilators, infusion pumps, and monitoring devices. The sterile environment minimizes the risk of infections and facilitates efficient patient care.
ICU Bed and Charges
ICU beds are specialized hospital beds with adjustable settings to enhance patient comfort and facilitate medical procedures. The ICU bed price in Delhi varies based on hospital facilities and bed type. The ICU charges per day depend on the level of care required, including ventilator support and specialized monitoring.
Difference Between ICU and CCU
Many people confuse the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) with the Critical Care Unit (CCU). While both provide life-supporting treatments, they cater to different patient needs.
| Feature | ICU (Intensive Care Unit) | CCU (Critical Care Unit) |
| Primary Focus | General critical care for various conditions | Specialized care for cardiac patients |
| Common Patients | Respiratory failure, trauma, sepsis | Heart attacks, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest |
| Ventilator Use | Frequently used | Occasionally used |
| Equipment | Ventilators, dialysis machines, monitors | ECG machines, defibrillators, cardiac monitors |
Choosing the Right ICU Hospital in Delhi
When selecting an ICU hospital in Delhi, consider the following:
- Advanced ICU Equipment – Hospitals with modern ventilators, monitors, and life-support systems offer better patient outcomes
- Specialist Availability – Look for hospitals with 24/7 critical care specialists and respiratory therapists
- ICU Bed Availability – The ICU bed hospital in Delhi should have adequate space for emergency admissions
- Affordability – Compare ICU charges per day across hospitals to ensure cost-effective care
Knowledge of ICU ventilation types and ventilator modes allows doctors to provide top-quality care to critical patients. Each ventilation method includes invasive and non-invasive techniques, volume-controlled, and pressure-controlled modes to get different treatment outcomes. The recovery of patients depends heavily on appropriate ICU equipment, monitoring, and a functional ICU setting.
Advanced critical care patients require state-of-the-art ICU facilities. Primus Super Specialty Hospital in Delhi is the best option for you. We are supported by skilled doctors and latest technology. Contact us today to get the best intensive care services.